 July 14, 2016. IFA News.
July 14, 2016. IFA News.
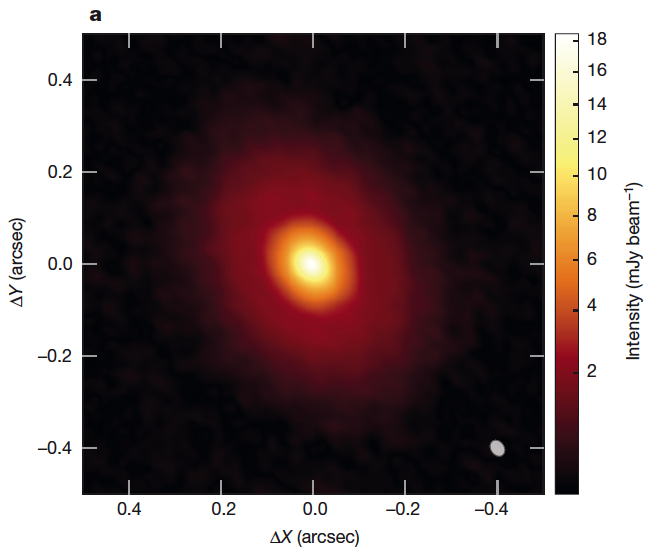
Prestigious NATURE published yesterday (July 14, 2016) an important discovery for the development of proto plnanetary discs and planet formation. The results belong to a study in which Claudio Cáceres, Héctor Cánovas y Matthías Schreiber, members of the Instituto de Física y Astronomía, IFA, participated. A snow-line is the region of a proto planetary disk at which a major volatile, such as water or carbon monoxide, reaches its condensation temperature. Snow-lines play a crucial role in disk evolution by promoting the rapid growth of ice-covered grains. Signatures of the carbon monoxide snow-line (at temperatures of around 20 kelvin) have recently been imaged in the disks surrounding the pre-main-sequence stars TW Hydra and HD163296, at distances of about 30 astronomical units (AU) from the star. But the water snow-line of a protoplanetary disk (at temperatures of more than 100 kelvin) has not hitherto been seen, as it generally lies very close to the star (less than 5 AU away for solar-type stars). Water-ice is important because it regulates the efficiency of dust and planetesimal coagulation, and the formation of comets, ice giants and the cores of gas giants. Here we report images at 0.03-arcsec resolution (12 AU) of the protoplanetary disk around V883 Ori, a protostar of 1.3 solar masses that is undergoing an outburst in luminosity arising from a temporary increase in the accretion rate. We find an intensity break corresponding to an abrupt change in the optical depth at about 42 AU, where the elevated disk temperature approaches the condensation point of water, from which we conclude that the outburst has moved the water snow-line. The spectral behaviour across the snow-line confirms recent model predictions: dust fragmentation and the inhibition of grain growth at higher temperatures results in soaring grain number densities and optical depths. As most planetary systems are expected to experience outbursts caused by accretion during their formation, our results imply that highly dynamical water snow-lines must be considered when developing models of disk evolution and planet formation. Image: credits Nature Magazine.
Associated link: Nature Magazine : Imaging the water snow-line during a protostellar outburst, .pdf file


 16/05/20019 Este viernes 17 de mayo se viene con un panorama de otro planeta, con el show astronómico de la banda Cósmic Strings integrada por varios investigadores del Instituto de Fisica y Astronomia. La actividad, de entrada liberada, tendrá lugar a las 23:00 horas en el Bar Cívico, ubicado en calle Blanco 1273, Valparaíso, cercano a la estación Bellavista del Metrotren. La música inspirada en planetas y...
16/05/20019 Este viernes 17 de mayo se viene con un panorama de otro planeta, con el show astronómico de la banda Cósmic Strings integrada por varios investigadores del Instituto de Fisica y Astronomia. La actividad, de entrada liberada, tendrá lugar a las 23:00 horas en el Bar Cívico, ubicado en calle Blanco 1273, Valparaíso, cercano a la estación Bellavista del Metrotren. La música inspirada en planetas y... 16/05/2019 Como ya es tradición, el viernes 24 de mayo, el Instituto de Física y Astronomía formará parte de la Feria de la Ciencia que cada año la Universidad de Valparaíso realiza para público escolar de la región. El objetivo es ofrecer a escolares y comunidades locales una muestra de actividades prácticas de investigación y formación en un espacio académico. Los alumnos tienen la po...
16/05/2019 Como ya es tradición, el viernes 24 de mayo, el Instituto de Física y Astronomía formará parte de la Feria de la Ciencia que cada año la Universidad de Valparaíso realiza para público escolar de la región. El objetivo es ofrecer a escolares y comunidades locales una muestra de actividades prácticas de investigación y formación en un espacio académico. Los alumnos tienen la po... 14/05/2019 La comuna de Calle Larga, distante 137 kilómetros de Valparaíso y sólo 75 de Santiago, inicia su despegue como nuevo epicentro astronómico de la zona central del país gracias al desarrollo que ha experimentado el Observatorio Pocuro, ubicado en el Centro Cultural Pedro Aguirre Cerda.
Este camino se ha ido pavimentando con la colaboración de la Universidad de Valparaíso, al establecer una...
14/05/2019 La comuna de Calle Larga, distante 137 kilómetros de Valparaíso y sólo 75 de Santiago, inicia su despegue como nuevo epicentro astronómico de la zona central del país gracias al desarrollo que ha experimentado el Observatorio Pocuro, ubicado en el Centro Cultural Pedro Aguirre Cerda.
Este camino se ha ido pavimentando con la colaboración de la Universidad de Valparaíso, al establecer una... 14/05/2019 La Dra Maja Vuckovic participará como expositora en la escuela de verano “Pulsaciones Estelares a lo largo de la evolución estelar” que se llevará a cabo en La Plata, Argentina entre el 11 y el 22 de noviembre.
El evento es una de las actividades astronómicas del año destacadas por el Boletín de Estrellas Masivas (Massive Star Newsletter) y se enmarca como parte del proyecto POEMS, Marie Curie Horizon 2020, d...
14/05/2019 La Dra Maja Vuckovic participará como expositora en la escuela de verano “Pulsaciones Estelares a lo largo de la evolución estelar” que se llevará a cabo en La Plata, Argentina entre el 11 y el 22 de noviembre.
El evento es una de las actividades astronómicas del año destacadas por el Boletín de Estrellas Masivas (Massive Star Newsletter) y se enmarca como parte del proyecto POEMS, Marie Curie Horizon 2020, d...
 10/05/2019 Utilizando observaciones submilimétricas del disco de escombros alrededor de la estrella debaja masa TWA 7, un grupo internacional de astrónomos liderado por la investigadora del IFA y Directora del NúcleoMilenio de Formación Planetaria Amelia Bayo, concluyó que la arquitectura asumida para esteobjeto es diferente a lo qu...
10/05/2019 Utilizando observaciones submilimétricas del disco de escombros alrededor de la estrella debaja masa TWA 7, un grupo internacional de astrónomos liderado por la investigadora del IFA y Directora del NúcleoMilenio de Formación Planetaria Amelia Bayo, concluyó que la arquitectura asumida para esteobjeto es diferente a lo qu...